活動目的
ACTIVITY PURPOSE
KEIO SPORTS SDGs について
KEIO SPORTS SDGs (慶應スポーツSDGs) は慶應義塾のスポーツ・運動・身体活動を担う専門部門と関連部門の横断型プラットフォームです。 下記の図のような身体活動の要素 (生活活動、スポーツ活動、レクリエーション活動) を含む様々な活動を広義に“スポーツ”と捉え、それらの促進と、SDGs達成に向けた活動を行っています。
スポーツ = 身体活動
SPORTS & PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
スポーツは、スポーツ活動に加え、
レクリエーション・生活活動における様々な身体活動を含みます
- スポーツ活動全般
- 定期的なサイクリング、スイミング、筋トレ、フィットネストレーニング、競技スポーツ(野球・サッカー・テニスなど)、個人スポーツ、学校体育など
- レクリエーション活動
- 余暇時間のウォーキング、ジョギング、サイクリング、遊び、ダンスなど
- 生活活動
- 通勤、通学、買い物、荷物運搬、掃除、選択、階段昇降、雪かき、農作業、ガーデニング、洗車、犬の散歩、子供と遊ぶなど
VISION
KEIO
慶應義塾が持つ強みを活かして
SPORTS
多様なスポーツ活動によって
SDGs
持続可能な開発目標の達成に貢献する
MISSION
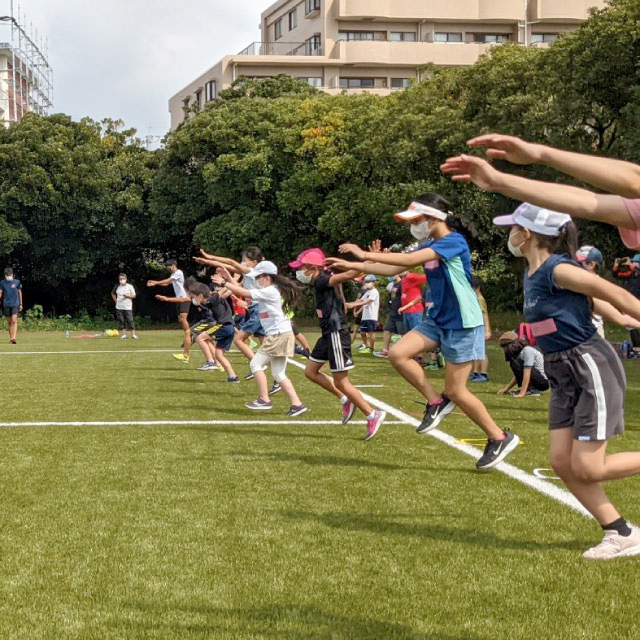

- 多様なスポーツの価値の普及
- KEIO SPORTS SDGsは、全世代および能力の制限のある方々を含む全ての人々がスポーツ(Sports &physical activities) に関与できる社会のためにスポーツの持つ価値を普及します。
- 社会課題解決への貢献
- KEIO SPORTS SDGsは、スポーツを通じた環境保護、健康促進、教育支援など、さまざまな社会課題への解決策を提供し、持続可能な開発目標に貢献します。
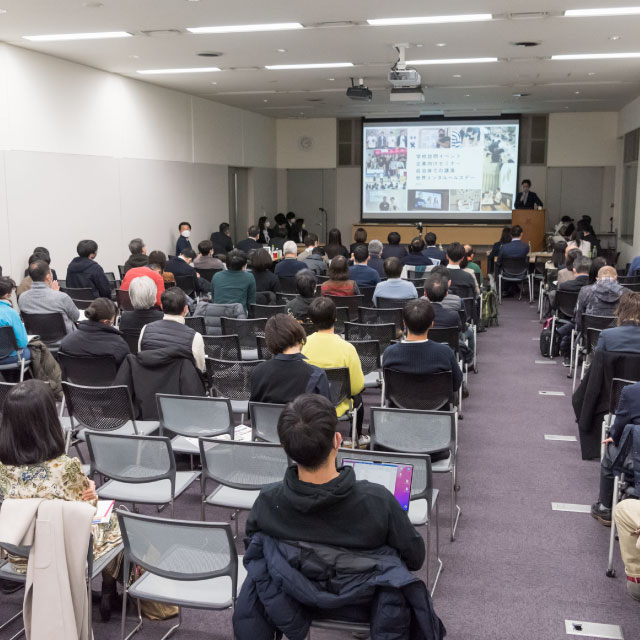

- 関係性の強化と共創の促進
- KEIO SPORTS SDGsは、システムズアプローチを活用し、普遍的かつ俯瞰的な視点でステイクホルダー間の関係性を強化し、共創を生み出します。
VALUE
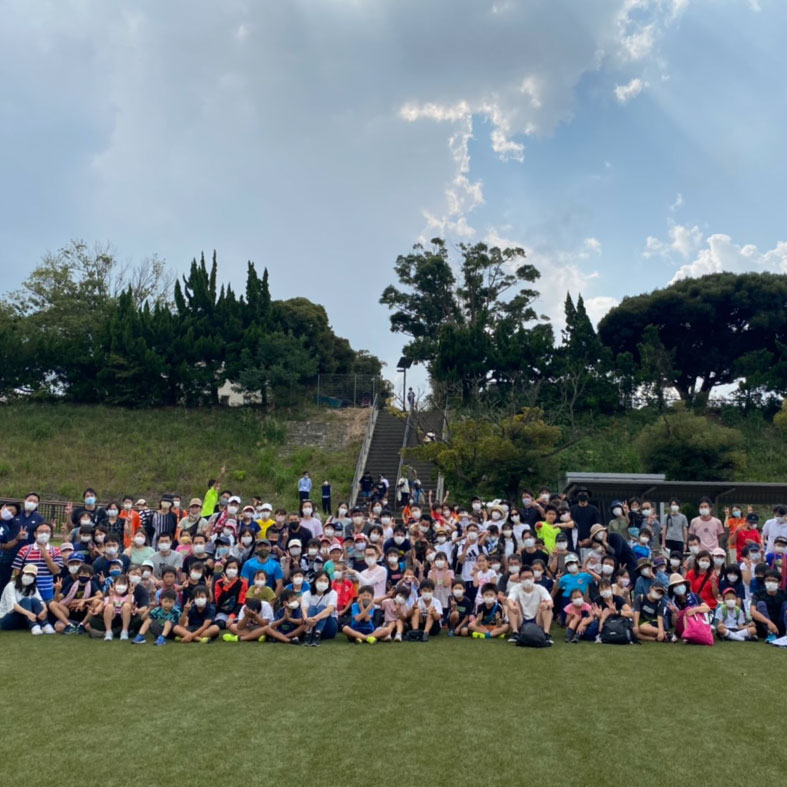

- システムズアプローチによる物事の理解と創造
- 地域スポーツ・身体活動からハイパフォーマンススポーツまで幅広いレベルのスポーツを統合的に扱い、システムズアプローチでスポーツと社会のつながりを可視化し、理解を深めることで、人材育成やプログラムデザインを通じてコミュニティ形成活動に積極的に貢献する。
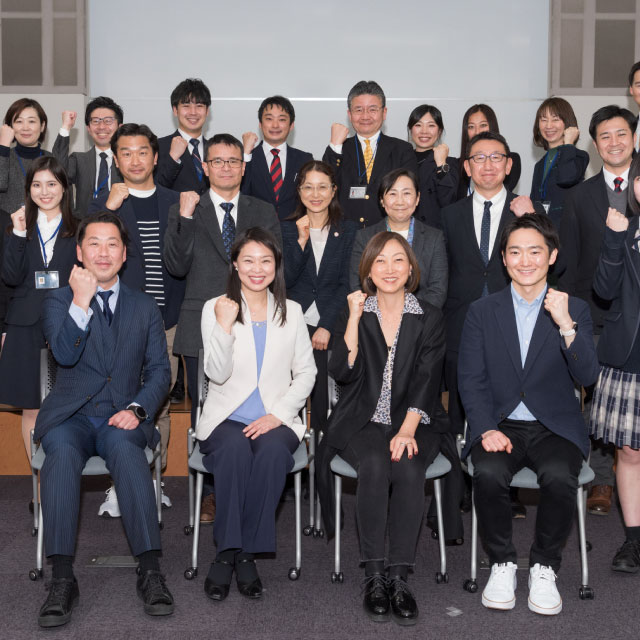

- 継続性のある多世代および多分野による共創
- 初等教育から高等教育(大学院教育)までの一貫教育と多様な分野に渡る14大学院・10学部および病院・研究所による多世代・多分野連携から、未来につながる未来を担う人材を育てる